Production Division Workflow
The Production Division is responsible for the production, water treatment, distribution and ensuring sufficient quantity of potable water for its consumers. It is likewise responsible for maintaining and improving the District’s Water Treatment Plant, Fourteen (14) Pumping Stations, and four (4) Elevated Reservoirs for its continued reliable and efficient operation.
It is supervised by the Production Division Manager who is responsible for the direction, supervision, management and control of all its personnel, likewise for the smooth operation and maintenance of the Water Treatment Plant Facilities, supplies, treatment, storage and distribution of potable water.
The Raw Water Generation Section is responsible for monitoring operation and maintenance of pumping stations ensuring effective water sources protection and sustainability as well as the efficient transmission of raw water to the treatment plant. They also conduct flushing operations on blow-offs/fire hydrants to safeguard the stability of water quality. They are also responsible for the maintenance, sanitation and cleanliness of WTP, pumping stations and reservoirs’ grounds and premises. Under this section are the Water Resources Facilities Operators (WRFO)/Pump operators, Watchmen and Guards.
The Water Treatment and Distribution Section is responsible for the treatment process of raw water and distribution to consumers. They also perform engineering task in the area of communication, instrumentation, controls and WTP monitoring system, the operation and monitoring of the central control and the Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) system. They operate the treatment plant and monitor the treated water distribution on a 24-hour basis based on system demand and monitor the treatment process according to current plant operating parameters. Under this section are the Water Utilities Development Officers (WUDO)/SCADA Operators and Chemical Handling Personnel/Plant Helpers whose functions includes mixing of chemicals for water treatment, assist in the routine maintenance on all WTP equipment and appurtenances and perform utility tasks at WTP premises.
The Quality Control/Assurance Section is responsible for the treatment of raw water including qualification, inspection, jar testing and treatment optimization of chemicals as well as supervision of Chemical Handling Personnel in the mixing of chemicals used for treatment. This section is also responsible for water testing relative to physical, chemical and bacteriological aspects ensuring supply of safe, potable water for its consumers. Handles water quality customer service and conducts researches on applicable technology and process to enhance water quality. Under this section are the Sr. Quality Control/Assurance Inspectors and Laboratory Aide.
WATER TREATMENT PROCESS DESCRIPTION
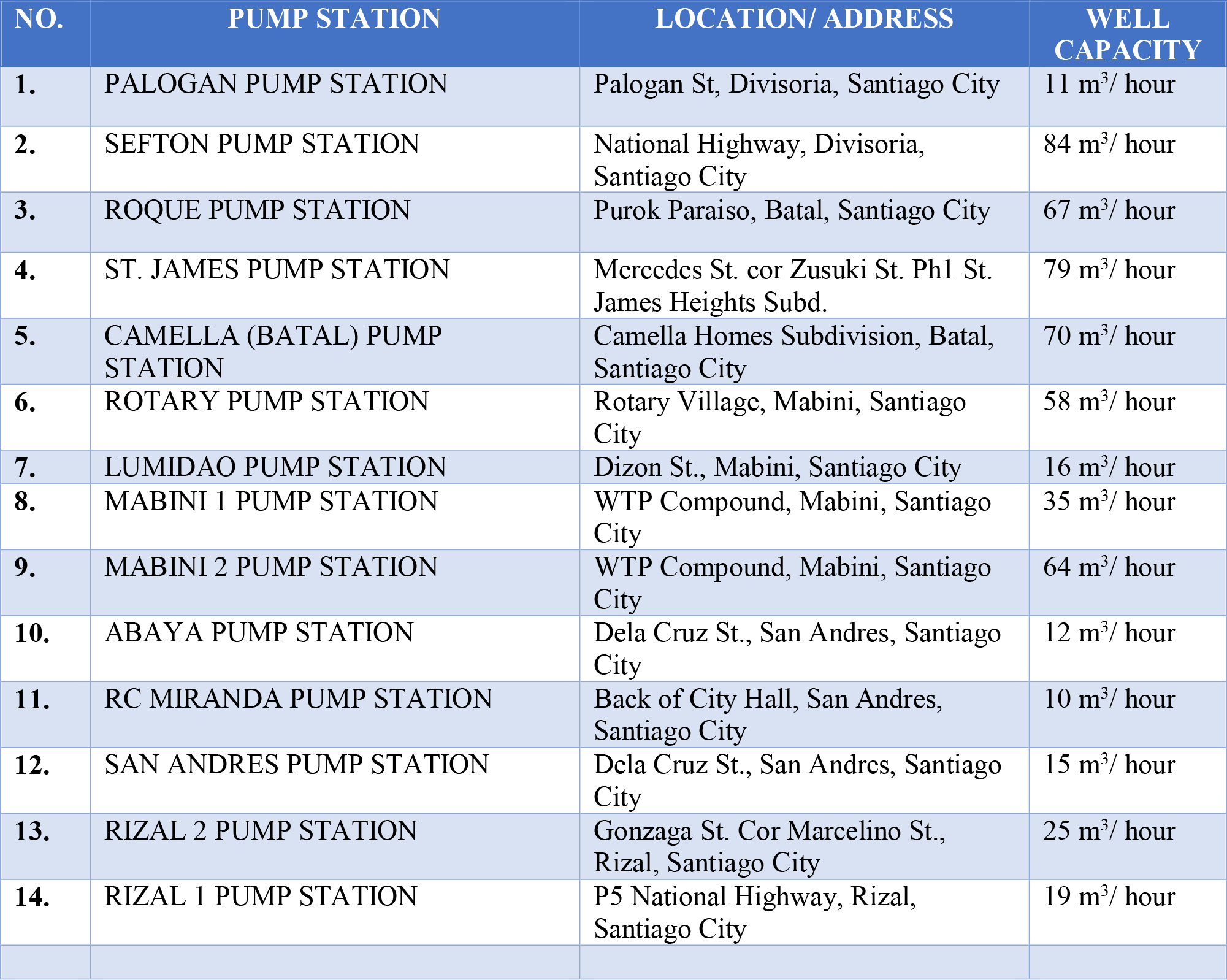
SANWAD’s water are sourced out from fourteen deep wells namely, Palogan, Roque, Sefton, St. James, Camella, Rotary, Lumidao, Mabini 1, Mabini 2, Abaya, San Andres, RC Miranda, Rizal 1 and Rizal 2. The total output of the 14 pumping station is ±580 cubic meters per hour. All sourced out raw water are conveyed to the Water Treatment Plant via Transmission Lines with pipe sizes ranging from 4” to 12” in diameter.
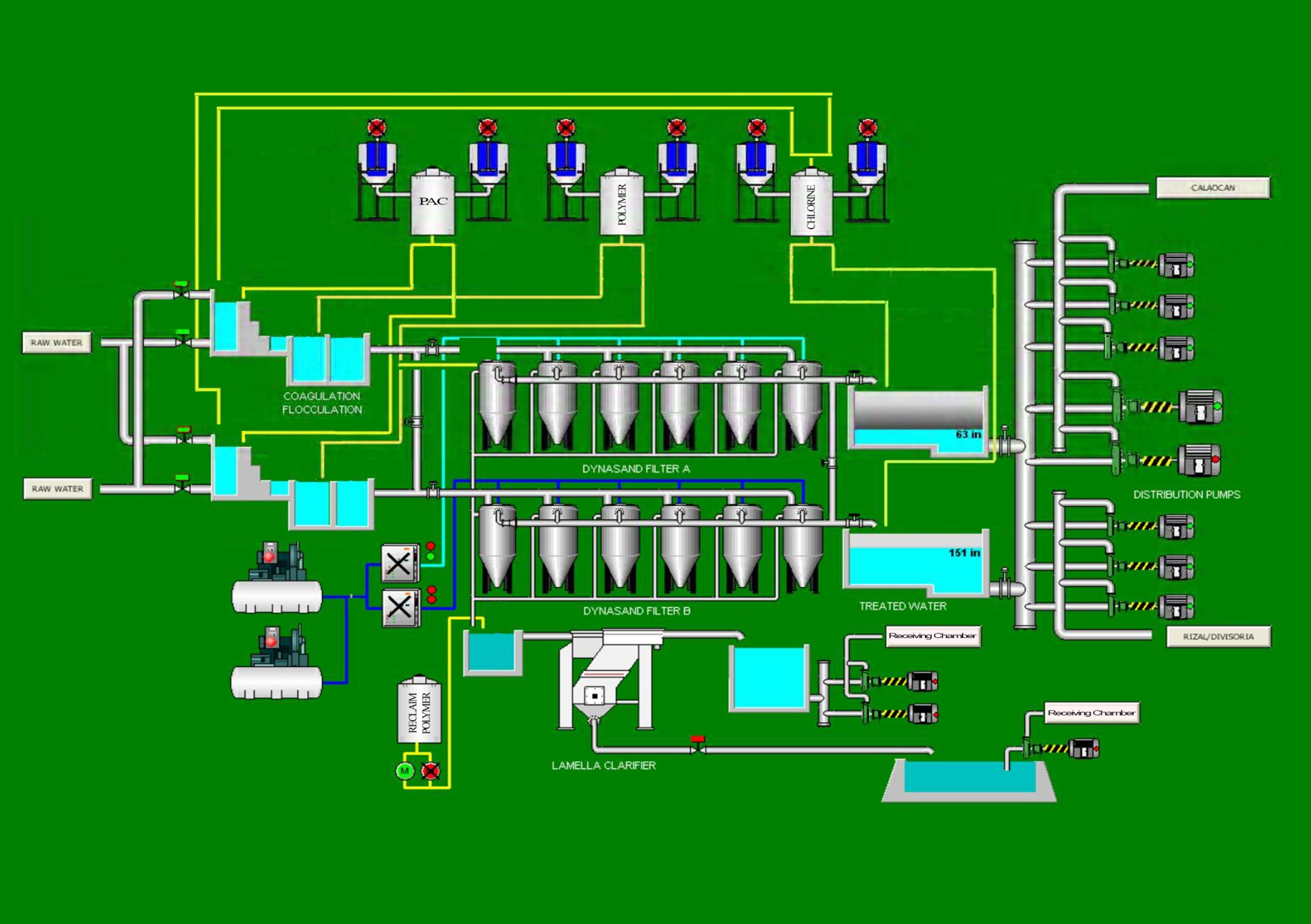
Raw water is then collected to two Receiving Chambers. Calcium Hypochlorite or Chlorine is injected here to facilitate partial oxidation. Each receiving chamber is provided with a baffle to facilitate initial sedimentation of undissolved solids in the raw water.
Water then passes through the baffle and on to two parallel streams of Cascade Aerator. Each Aerator has three cascade falls which enables partial oxidation of dissolved iron in the raw water. Polyaluminum Chloride (PAC) which acts as a coagulant in the water treatment process is injected at the top of the Cascade Aerator. To protract the contact time of the injected PAC in the water, the Production Division innovated a means to enable the same. Concrete blocks where installed at the edge of each cascade falls in order to divert water to a smaller opening before the water drops to the next cascade. Hence, a longer contact time between the water and PAC will be achieved. A collection basin at the bottom of the cascades collects the aerated and coagulated water which will then be channeled to the next stage.
Following the Cascade Aerator streams are the Coagulation Chambers. As per design, these chambers are where the PAC chemicals are supposed to be injected. But present circumstances dictate that remodeling or the adaption of modified stages in the treatment process be implemented. Thus, the Production Division deemed it necessary to implement its redesigned process flow in order to be attuned with the current requirements in the treatment of raw water. As such, the Coagulation Chambers were modified to act as the Flocculation Chambers where Anionic Polymer is injected. The water has a detention time of 16 minutes in order to aid complete reaction of chemicals (e.g. PAC and Polymer) resulting to a full build-up of flocs.
Following the now Flocculation Chambers are the previous ones. It operates now as a Clumping Chamber to further increase floc mass build-up for improved filtration on the succeeding stage. Like the Receiving Chamber, it also functions as a sedimentation chamber because of the integrated baffle where water passes through prior to filtration.
Chemically reacted water is immediately fed by gravity to 12 units of Dynasand Filter. As the name implies, water filtration is its lone function. It filters out the mass of flocs in the water together with iron and other particulate precipitates. Each train has 6 units which is supplied individually with 4 bars of compressed air to effect continuous cleaning of the filter media. The filter media in each filter tank is 7.3 cubic meters of graded river sand which is replenished every year for maximum filtration. As the influent flows upward, solids are trapped in the sand bed. The filtrate exits over an effluent weir at the top of the filter. Simultaneously, the sand bed, along with the accumulated solids is drawn downward into the airlift pipe which is located in the center of the filter. A small volume of compressed air is introduced at the bottom of the airlift. The air rises, draws the sand into the airlift and scours the sand of trapped particles and excess biomass. Wash water from each Dynasand filters goes directly to a flash mixing tank where Anionic Polymer is again injected for sedimentation purposes on its integrated Clarifier.
A lamella clarifier works when a solid/liquid stream that has been flocculated, enters a tank, and flows upward between a pack of inclined plates. The solids fall to the plate surface, where they slide by gravity down to a sludge collection hopper. The clarified effluent flows through orifice holes and exits the top of the settler.
After undergoing filtration, water again flows by gravity to two Treated Water Tanks with a capacity of 725 cubic meters each. Further injection of Chlorine is made here for disinfection purposes, which completes the treatment process of the water to be distributed to all consumers. Baffles are integrated at both treated water tanks to facilitate appropriate contact time for the chlorine.
Distribution pumps are used to boost the treated water to its consumers. There are two main distribution lines. The line with the biggest coverage is the Calaocan Reservoir line. Said Reservoir functions as a “fill and draw” reservoir and is operating by gravity distribution. It covers the greater Business District of the City. The second is the Rizal/Divisoria Line which has two “floating-on-the-line” reservoirs and operates through direct pumping.
The Calaocan Reservoir line has two overhead reservoirs with a capacity of 550 cubic meters each. The Floating-on-the-line Reservoir at the Rizal line has a capacity of 500 cubic meters and 350 cubic meters for the Divisoria reservoir. A retrofitted concrete reservoir at the Poblacion area is undergoing commissioning works as of the moment and will serve the higher areas of the same.
Part of SANWAD’s innovation on the existing design of the Water Treatment Plant is the incorporation of a “Waste Water Recycling System.” It utilizes the sludge lagoon as a clarifying facility wherein waste water undergoes clarifying procedures before being recycled and pumped back to the receiving chamber.
The waste water undergoes three clarifying stages wherein sludge and any other undissolved solids are separated.
The whole process from the raw water source and up to the storage reservoirs are monitored and controlled through a Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) system. A SCADA system is a human-machine-interface with a graphic display on the computer monitor which represents the different components of the treatment process. It is the link between the on-duty Water Utilities Development Officer and the machine. It provides real time status and control of the different components of the water generation section, water treatment process and the reservoir status.
Water quality is closely monitored by on-duty Quality Control and Assurance personnel on a 24 hour cycle. Prior to distribution, water quality is regularly tested at the distribution header as well as on all stages of the treatment process to ensure compliance to the requirements of the Philippine National Standards for Drinking Water (PNSDW). Parameters for monitoring water quality include pH, conductivity, turbidity, color, residual chlorine, iron, residual alumina, microbiological test, TDS, manganese, sulfate and chloride.
SANWAD’s quality monitoring doesn’t stop at the Water Treatment Plant. Laboratory personnel conduct daily monitoring of water quality right at the tap of every consumer. Again, this is to ensure excellent quality of potable water in every household.
The Laboratory Section of SANWAD likewise performs random tests in different areas for microbial organisms in the water coming from the tap of every household, thus preventing the occurrence of possible illnesses at a certain time.
PUMPING STATIONS as of December 31, 2018
Location Map of SANWAD Facilities

SANWAD Water Treatment Process
SANWAD WTP Process Flow
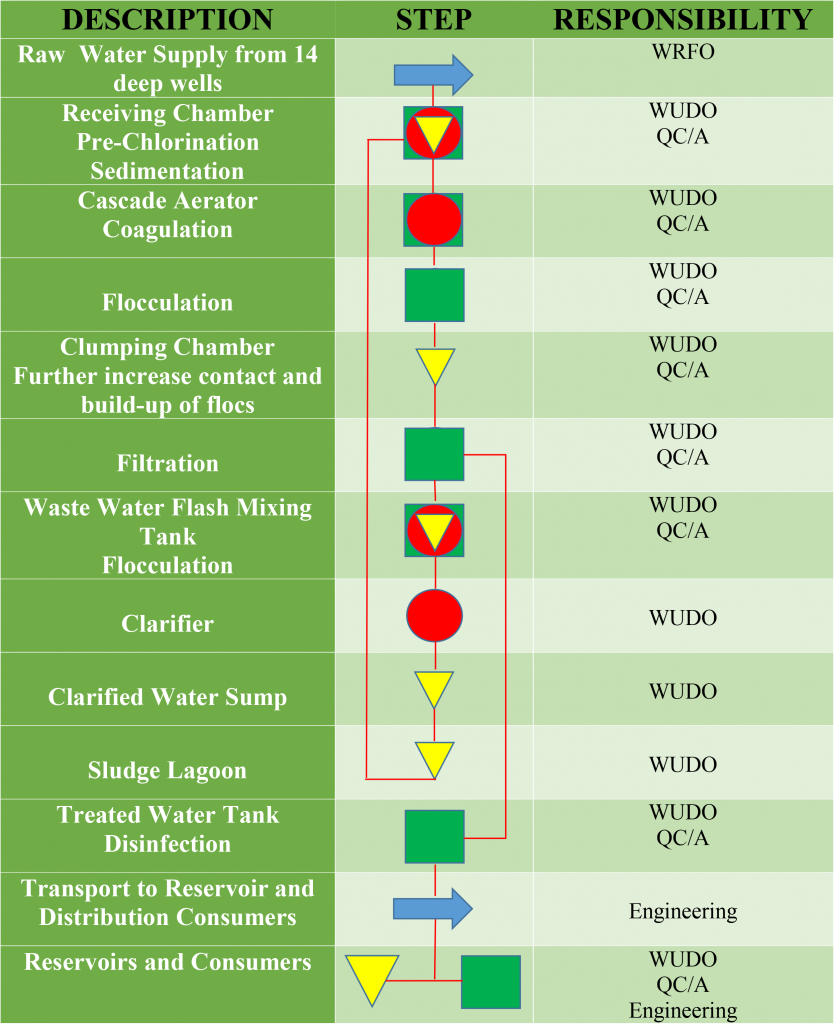
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES DURING HAZARDOUS EVENT
The Water Treatment and Transmission Section of the Production Division shall implement the Standard Operating Procedure when hazardous events occur at any part of the water treatment process. Whenever necessary, the Property Supply Office of the Admin/Finance Division shall provide the needed materials or equipment to address major incidents.

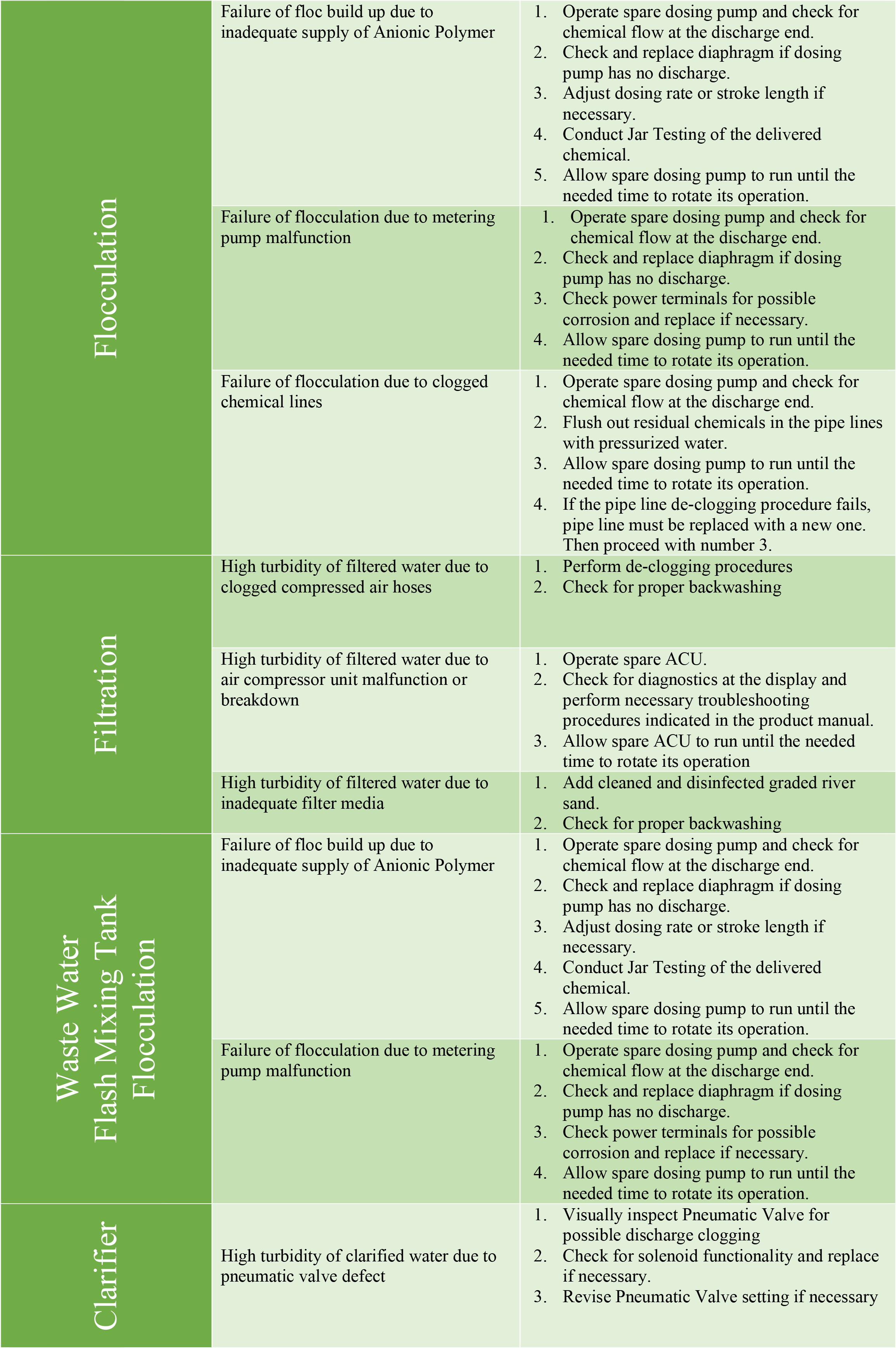
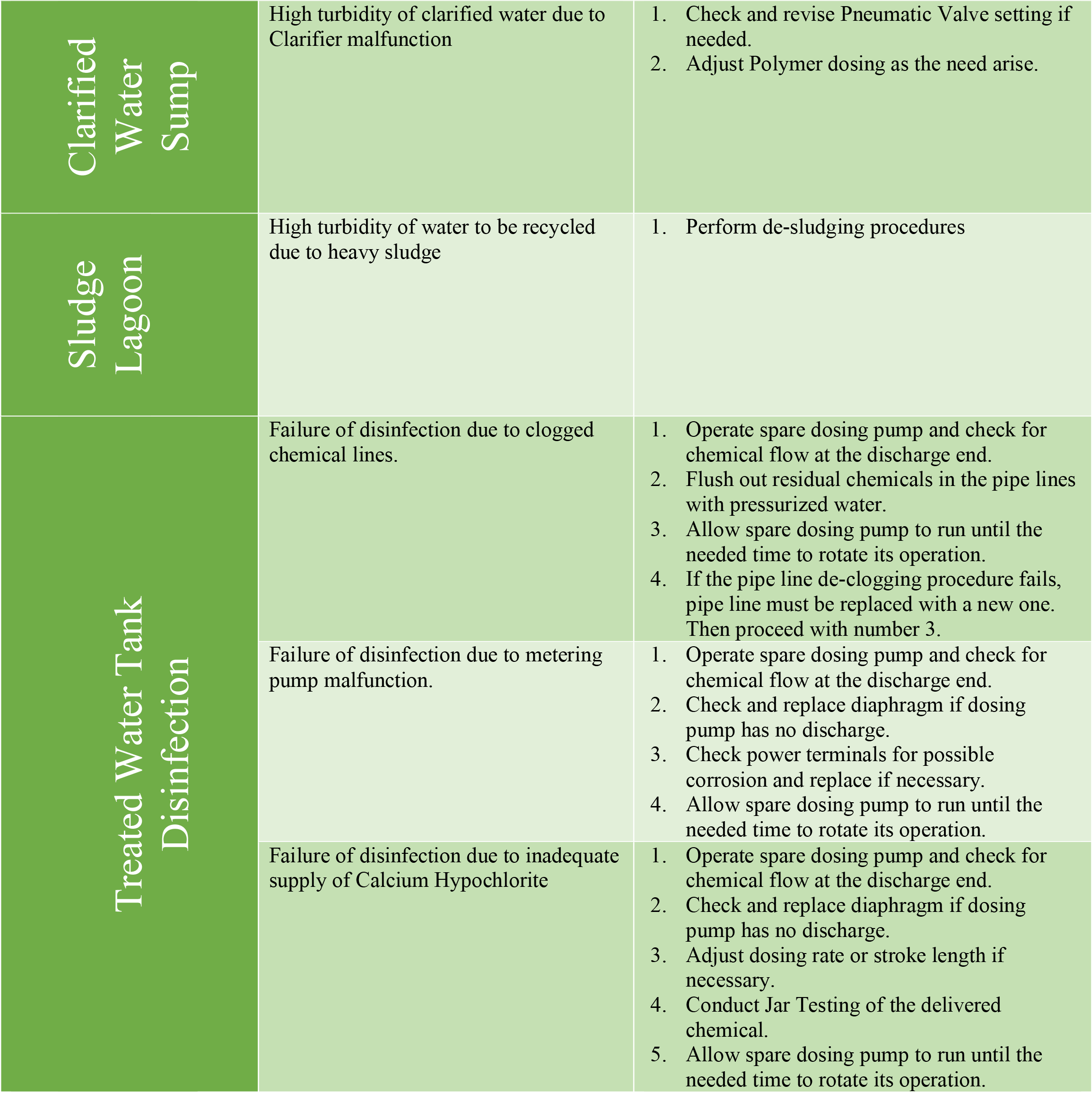
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES DURING NORMAL OPERATION
The Water Treatment and Transmission Section Personnel and the Water Quality/Assurance Section Personnel of the Production Division shall implement the Standard Operating Procedure during normal operations at any part of the water treatment process.
In doing so, the Water Treatment and Transmission Section personnel regularly conducts preventive maintenance procedures as its Standard Operating Procedure. Regular checking and maintenance of all dosing pumps as well as periodic flushing of all chemical pipelines are conducted daily. Dosing pumps are operated alternately to mitigate motor overworking and excessive heating. All chemical mixing and day tanks are cleaned on a weekly basis. Preventive Maintenance on all its electrical components are also conducted on a semi-annual frequency.
The water treatment facility is drained, cleaned and disinfected once a year to prevent heavy build-up of sediments and sludge. The filtration facility likewise undergoes preventive maintenance through the periodic checking of both Air Compressor Units. Likewise, both Air Compressor Units are operated alternately to mitigate motor overworking and excessive heating.
The Water Quality /Assurance Section personnel also maintains a buffer supply of chemicals to ensure water quality. The amount of chemical injected in the water treatment process is monitored and tested once per shift and the residual chlorine is likewise examined four times per shift.
SANWAD – WATER LABORATORY SERVICES
General information
The Santiago Water District-Water Laboratory is authorized to operate by virtue of Board Resolution No. 67-2012 and accredited under Administrative Order No. 2006-004: Rules and Regulations Governing the Accreditation of Laboratories for Drinking Water Analysis and EO 102 dated May 2, 1999: Redirecting the Functions and Operations of the Department of Health.
Competent Department of Health-National Reference Laboratory (DOH-NRL) and University of the Philippines-Microbiological Research and Services Laboratory trained analysts, standard procedures, modern equipment, careful testing, guarantee results with accuracy. We comply with the DOH standards, Philippine National Standards for Drinking Water, and our mission thru hard work and dedicated service.
Participated and passed the annual Proficiency Testing conducted by DOH-NRL with acceptable and excellent results since 2012. Excellent service, modern facility and high quality standard laboratory equipment.
SANWAD Water Laboratory caters water districts and other water service providers, water refilling stations, hospitals, restaurants, fast food chains, schools, birthing clinics, dialysis centers, households, etc.
Microbiological Testing Rate
Package Rate- PhP 450.00/sample
*Total Coliform Test (Multiple Tube Fermentation Technique)
*Fecal Coliform Test (Multiple Tube Fermentation Technique)
*Heterotrophic Plate count (HPC)
Others:
Sterile Bottle – PhP 65.00
Procedure in availing our services
-
Proceed to SANWAD Main Office Cashier for payment of the testing fee & sterile bottle.
Provide the name of the company & owner, address, and number of samples for testing.
-
The Cashier will issue official receipt, sterile bottle/s & sampling procedure for first time clients.
-
Collect water sample following the procedure then proceed to SANWAD Water laboratory. Present the Official Receipt & submit the water sample with label indicating sample source, date & time of collection, name of person who collected/submitted the sample.
-
Results will be released after five (5) workings days from the date of submission.
Note: Water sample should be taken on the day of testing. Maximum holding time is six (6) hours after collection. The use of ice coolers for storage of water sample during transportation to the laboratory is recommended. The time elapsed between collection and processing should in no case exceed 24 hours.
Schedule of Bacteriological Testing:
8:00AM-12:00PM Only- For submission of water samples
8:00AM-5:00PM- For claiming of results
Releasing of Results
Five (5) workings days after submission of water sample/s.
No Official Receipt. No release of result.





